
Analytics Consulting
NTT DATA created an analytics methodology called BICLAVIS by leveraging the expertise acquired from 200 business intelligence (BI) consulting cases.
NTT DATA created an analytics methodology called BICLAVIS by leveraging the expertise acquired from 200 business intelligence (BI) consulting cases.
BICLAVIS defines 4 types of business intelligence and 9 scenario patterns:
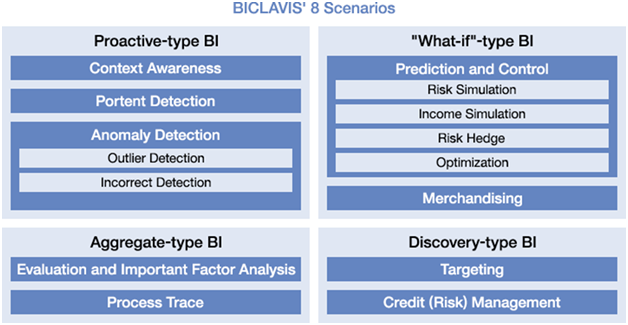
1) Proactive-type BI: Understand and predict users’ behavior to proactively provide targeted services or functions.
Scenarios:
- Context Awareness: Recommend the service through the analysis of users’ behavior and preference.
- Portent Detection: Detect the portent of changes by monitoring users’ behavior and status.
-
Anomaly Detection
- Outlier Detection: Detect the outliers in a dataset that satisfy defined rules.
- Incorrect Detection: Detect the deviation by matching the rule defined in the normal situation.
Examples of applications: Recommendation systems, anomaly detection.
2) What-if-type BI: Design new business logics and evaluate them by numerical simulation.
Scenarios:
-
Prediction and Control
- Risk Simulation: Assess risks by business modeling and uncertainties.
- Income Simulation: Estimate the profits by work restructuring.
- Risk Hedge: Support the decisions by business modeling and optimization procedure.
- Optimization: Support the risk reduction by business modeling and the method of diversification of risk.
- Merchandising: Rank and allocate products to stores.
Examples of applications: Supply chain optimization, resource planning.
3) Aggregate-type BI: Aggregate and visualize accumulated data in various dimensions.
Scenarios:
-
Prediction and Control
- Evaluation and Important Factor Analysis: Weigh up the various objects and identify their factors.
- Process Trace: Extract the process of growth and development, and identify the accelerator or inhibitory.
- Merchandising: Rank and allocate products to stores.
Examples of applications: Planning task, supply-demand adjustment.
4) Discovery-type BI: Discover the correlation and rules among accumulated mass data by using data mining techniques.
Scenarios:
-
Prediction and Control
- Targeting: Extract information to target specific entities, e.g. potential customers.
- Credit (Risk) Management: Determine the default risk of individuals or the bankruptcy risk of companies.
- Merchandising: Rank and allocate products to stores.
Examples of applications: Customer scoring, risk quantification.




