
Transforming Materials Development Through Data Analytics:
What Is Materials Informatics?
In this article, we introduce an overview of Materials Informatics-a rapidly emerging field that is drawing increasing attention-and highlighting NTT DATA's initiatives in this area.
Traditionally, in fields such as drug discovery and new materials development, researchers have relied heavily on trial-and-error experimentation based on personal experience. As a result, development processes have often taken several years-or even more than a decade-to complete.
Today, there is growing interest in leveraging big data analytics to accelerate development speed and reduce costs. At NTT DATA, we are applying the expertise cultivated in our Labs and Innovation Centers to significantly shorten materials and molecules development cycles across multiple domains.
1. What is "Materials Informatics"?
Materials Informatics (MI) is the interdisciplinary field that leverages data analytics to accelerate and make materials development more efficient. Traditionally, materials research required long periods of experimentation through repeated trial and error. Chemists and materials scientists played a crucial role in designing experiments, interpreting results, and gradually identifying structure-property relationships that could lead to new materials or improved performance.
This approach, while scientifically rigorous, was often time-consuming, costly, and limited in the number of material combinations that could realistically be tested. In the era of Materials Informatics, data-driven methods do not replace this expertise - they amplify and accelerate it. MI analyzes vast amounts of historical experimental data and employs simulations coupled with high-throughput screening to identify promising material candidates more quickly.
MI has gained attention as a key paradigm that enhances development speed and reduces costs across various industries, thereby strengthening corporate competitiveness. Until recently, MI was limited by the lack of both large, high-quality experimental datasets and sufficient computational power to process them. Today, the convergence of accumulated experimental data with modern computational infrastructure-including high-performance computing and emerging quantum platforms-has finally made data-driven materials discovery feasible. Moreover, rapid advancements in data analytics technologies-such as AI and machine learning-, have further accelerated research and development in the MI field and transforming how materials research is conducted.
2. Technologies and Approaches Behind Materials Informatics
In 2019, NTT DATA established the Quantum Computing and Next-Generation Architecture Laboratory, and later, in 2022, launched the Innovation Center initiative, to foster research and innovation across strategic technology domains and to conduct numerous technical verifications in collaboration with various clients. Through these activities, it became clear that one of the major challenges in adopting MI lies in solving complex "optimization problems" - determining the best solution among an enormous number of possible combinations. In addition to optimization, MI also requires sophisticated data science pipelines that involve data preparation, model training, and simulation workflows-demanding strong software engineering expertise and the contribution of experienced system integrators. To address this, NTT DATA is leveraging the expertise of the laboratory to explore how such optimization problems and data science workflows can be solved efficiently using advanced computing platforms, including quantum computers.
At the same time, the successful implementation of MI requires not only IT technologies but also deep domain knowledge of materials development processes and evaluation methods. How data is collected, interpreted, and applied in R&D settings heavily depends on such expertise and on-the-ground understanding. Recognizing this, NTT DATA actively collaborates with partners - including universities and startup companies possessing specialized knowledge in materials science and chemistry - to co-create practical MI solutions through industry-academia partnerships.
3. Materials Informatics Use Cases at NTT DATA
The following sections present two case studies of NTT DATA's work in MI.
Accelerating CO2 Capture with AI - NTT DATA's Challenge to Speed Up Catalyst Discovery with Machine Learning and Generative AI
The urgent need to mitigate climate change has intensified research efforts in carbon capture and utilization technologies. The importance of this field was recently underscored by the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, awarded to Kitagawa, Robson, and Yaghi for developing metal-organic frameworks capable of efficiently capturing CO2.
This project, led by NTT DATA in collaboration with the University of Palermo and the University of Catanzaro, and funded by the Italian National Recovery and Resilience Plan within the ICSC center (https://www.supercomputing-icsc.it/en/icsc-home/) aims to accelerate the discovery and design of novel molecules that efficiently capture CO2 and catalyze its transformation into valuable chemicals: beyond materials that physically capture CO2, molecular catalysts offer a complementary approach by chemically activating and converting CO2 into valuable products, gaining significant attention for their tunability and catalytic efficiency.
By leveraging High-Performance Computing (HPC) and Machine Learning (ML) models, we seek to overcome traditional limitations in molecular screening and develop a systematic, data-driven framework for the design of innovative catalysts. Experimental approaches involving Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) are implemented to propose new molecular structures with optimized properties, broadening the search space beyond traditional design paradigms and accelerating chemical space exploration. Furthermore, Quantum Computing frameworks are investigated to assess their potential in accelerating and improving performance of GenAI techniques, with the long-term goal of adapting the computational workflow to emerging computational technologies. The project is now entering its final phase, with promising molecules for CO2 catalysis identified through the Materials Informatics workflow and currently under evaluation by the chemistry experts of our university partners.
In summary, our approach integrates Chemistry, Machine Learning and structural analysis through HPC to identify promising molecular structures that can enhance catalytic activity in CO2 capture. The protocol is eventually transferable to different systems, amplifying its impact beyond CO2 capture and conversion.
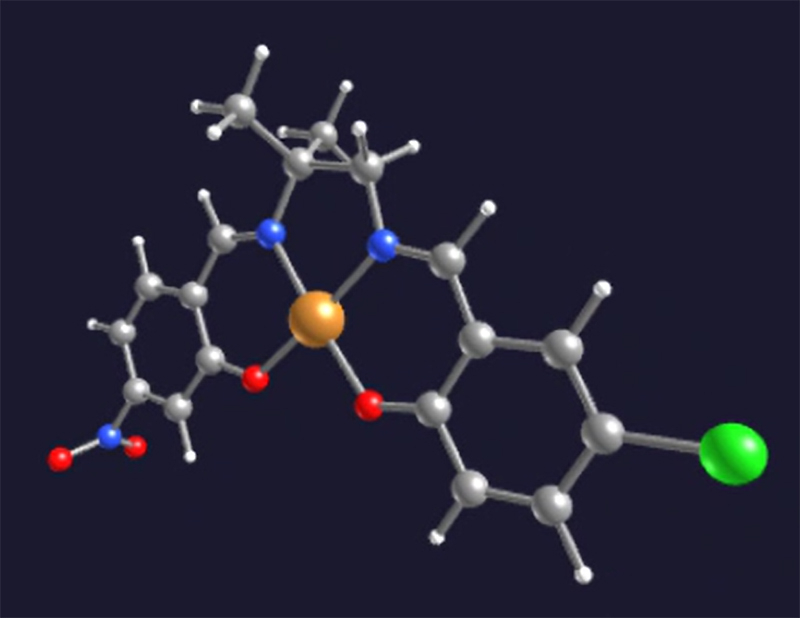
Fig 1. Examples of calculated molecular structures
Reproducing Scents with Data - NTT DATA and Komi Hakko's Challenge to Digitalize "Smell"
NTT DATA has been conducting joint research with Komi Hakko, a startup originating from Osaka University, since 2022. Komi Hakko is the world's first company to develop a technology that quantifies scents, enabling the reproduction of specific odors by blending multiple fragrance ingredients to match a target numerical profile.
However, since there are thousands of potential fragrance components, identifying the optimal combination among the countless possibilities posed a significant computational challenge.
To overcome this, NTT DATA combined its proprietary optimization technology, cultivated within its laboratory, with Komi Hakko's scent quantification technology. This collaboration has enabled the efficient exploration of scent composition patterns that would be difficult for humans to discover manually, and led to the development of a new formulation process for deodorant products that reduces production time by approximately 95% compared to conventional methods - achieving a remarkable improvement in the efficiency of material development processes.
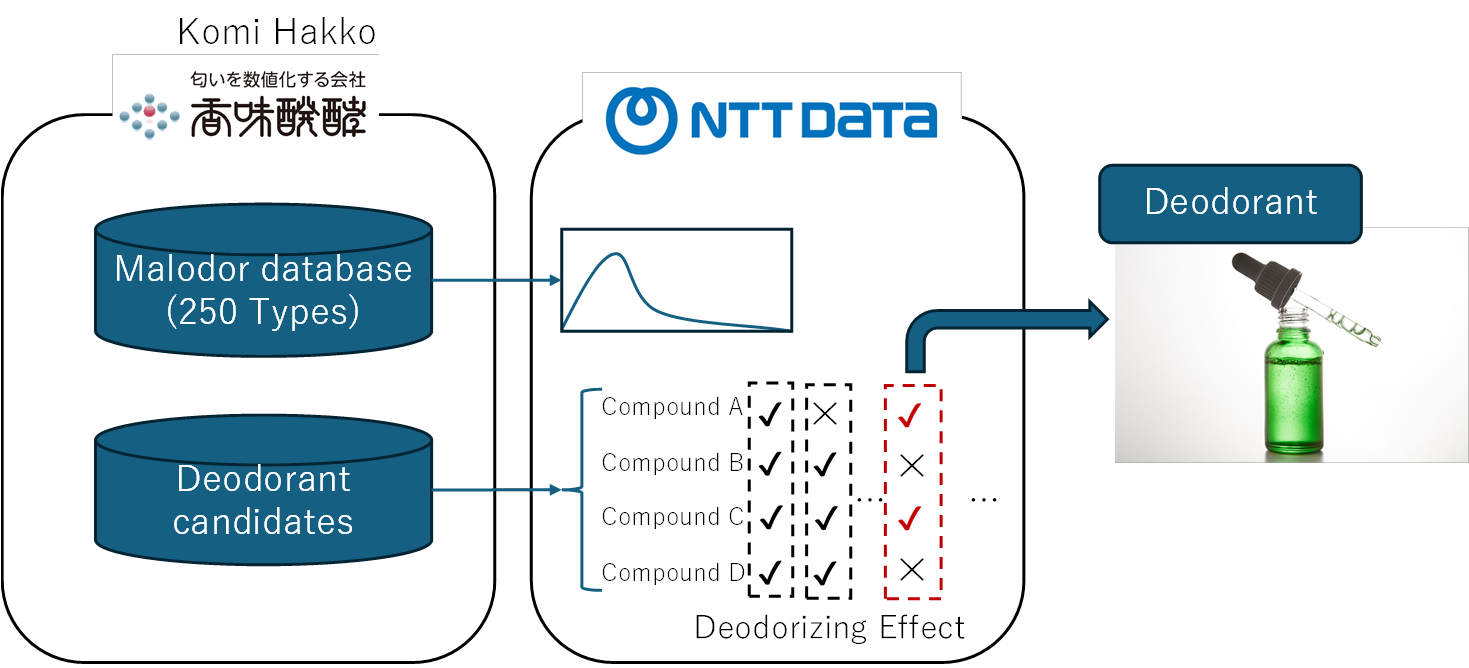
Fig 2, Image of deodorant formulation
4. Conclusion
In this article, we introduced an overview of Materials Informatics and NTT DATA's related initiatives.
Looking ahead, NTT DATA will continue advancing the application of cutting-edge technologies - including AI, high-performance computing, and quantum computing - to enhance materials development across various industries - including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and energy materials.
By integrating data-driven methods with domain expertise, we enable faster discovery timelines, achieve significant reductions in experimental time and costs, and identify previously undiscoverable materials-ultimately driving innovation and competitiveness in the next generation of materials research.

Mikiya Tanizawa
Senior Expert Innovation Center, NTT DATA Group Corporation
Since joining NTT DATA in 2011, Mikiya has been engaged in system development for financial clients, R&D on device utilization, collaboration with overseas startups, and global HR initiatives. Since 2023, he has been working at the Innovation Center where he focuses on creating new businesses by leveraging emerging technologies.

Antonio Policicchio
Innovation Engager Leader, PhD Advanced Technology & Innovation, NTT DATA Italia S.p.A.
With a PhD in Physics at the University of Calabria, Antonio has held post-doc and research positions at several universities and research institutes, including the University of Washington, CERN and Sapienza University of Rome. His research activities resulted in more than 1000 scientific papers published in prestigious journals and conference proceedings. In March 2020, he joined NTT DATA Italia within the Advanced Technology & Innovation business line. He leads the proposal and design of cutting-edge solutions that align with clients' digital strategies, with a particular focus on innovation and R&D projects in Artificial Intelligence, Digital Twin, and Quantum Computing
